Thyroid Resilience

Thyroid Resilience Is a Comprehensive, Thyroid Supportive Supplement from Progressive Laboratories
What Our Thyroid Resilience Is:
- Thyroid Resilience® is a scientifically designed and balanced nutraceutical encapsulated formulation that helps to stimulate the synthesis and systemic utilization of normal levels of the thyroid hormones, as well as to protect the thyroid gland and other vital organ systems from environmental toxicity and oxidative stress damage.
Why You Should Consume Our Thyroid Resilience:
- You should consume Thyroid Resilience in order to assist your body in the goal of having optimal thyroid function which is crucial to energy, heart function, weight management, mood and mental health, digestive function, reproductive health, and bone health.
- The completeness of the Thyroid Resilience product is the reason to choose it in particular. It contains virtually every ingredient known to science to assist the thyroid to function optimally.
- If you aren't feeling young and alive anymore, the first thing you should try is boosting Thyroid function. This product is your best bet.
No One Can Overstate the Importance of Thyroid Function - Without a Well Functioning Thyroid - Numerous Functions of the Body Will Never Be As Good as They Could Be
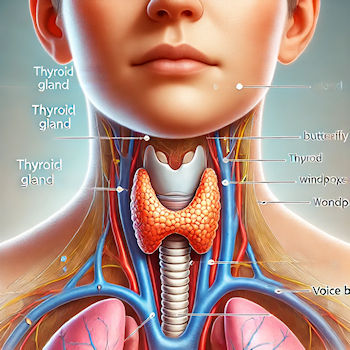
- The thyroid gland is crucial to energy and health because it plays a key role in regulating many vital functions in the body through the hormones it produces. Here’s why the thyroid is so important:
- Metabolism Regulation: the thyroid gland produces hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which control the body’s metabolism. These hormones regulate how the body uses energy, affecting everything from how fast you burn calories to how efficiently your organs function.
- Heart function: the thyroid hormones help regulate heart rate and the strength of heart contractions. When thyroid function is off, it can lead to heart-related issues like a fast or slow heart rate, high blood pressure, or even heart failure in severe cases.
- Body Temperature Regulation: The thyroid gland helps maintain normal body temperature. A healthy thyroid ensures that your body can adapt to changes in temperature by regulating the production of heat.
- Growth and Development: In children, thyroid hormones are essential for normal growth and brain development. An underactive thyroid during pregnancy or in young children can lead to developmental delays or growth problems.
- Mood and Mental Health: Thyroid function has a significant impact on mental health. Low thyroid hormone levels (hypothyroidism) can lead to depression, sluggishness, and memory problems, while high thyroid hormone levels (hyperthyroidism) can cause anxiety, restlessness, and mood swings.
- Weight Management: Because the thyroid regulates metabolism, it also affects weight. An underactive thyroid can slow metabolism, making it harder to lose weight.
- Digestive Function Thyroid hormones influence the speed at which food moves through the digestive tract. An underactive thyroid can cause slow digestion and constipation, while a stressed, overactive thyroid can lead to diarrhea or frequent bowel movements.
- Reproductive Health: The thyroid also plays a role in reproductive health. Thyroid imbalances can disrupt menstrual cycles in women and may affect fertility. Thyroid disorders during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications.
- Bone Health: Thyroid hormones help regulate the body’s use of calcium, impacting bone growth and strength.
Learn More About The Superior Ingredients of Thyroid Resilience
L-Tyrosine Is Important for the Thyroid and Overall Health for the Following Reasons
1. Supports Thyroid Function
Thyroid hormone production: Tyrosine, along with iodine, is a critical component in the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). These hormones regulate metabolism, energy, and overall well-being. Supplementing with tyrosine can support thyroid health, especially for those with low thyroid function (hypothyroidism), as long as iodine levels are adequate.
2. Improves Cognitive Performance Under Stress
Stressful situations: Tyrosine helps maintain mental performance during stressful or demanding situations. It is a precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine, which are involved in stress response and mood regulation. Tyrosine supplementation can support focus, alertness, and memory during periods of acute stress, such as sleep deprivation, multitasking, or extreme environments.
3. Boosts Mood and Mental Health
Dopamine production: Tyrosine is a precursor to dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a major role in mood regulation, motivation, and reward. Supplementing with tyrosine may help alleviate symptoms of depression or low motivation, especially in people with low dopamine levels.
Combats fatigue: Tyrosine can help improve mood and reduce fatigue, making it useful for individuals who feel mentally drained or overworked.
4. Enhances Physical Performance
Improves endurance and focus: Tyrosine can enhance mental and physical performance during physically demanding tasks. Athletes, especially those engaged in endurance activities or high-intensity training, may benefit from improved focus, faster reaction times, and better stress resilience during exercise.
Reduces exercise-related stress: Since tyrosine supports the production of stress-related neurotransmitters, it can help reduce the impact of physical stress during exercise, making it easier to maintain performance under tough conditions.
5. Supports Cognitive Function
Memory and learning: Tyrosine plays a role in cognitive functions like learning and memory. It may be beneficial for people who need to perform mentally demanding tasks, especially in situations where focus and alertness are critical (e.g., students, professionals under pressure).
Helps with ADHD: Since tyrosine boosts dopamine production, it may be helpful for individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), as dopamine plays a key role in regulating attention and focus.
6. Helps Manage Phenylketonuria (PKU)
PKU management: Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a genetic disorder that causes individuals to be unable to metabolize phenylalanine, an amino acid that converts to tyrosine. People with PKU may benefit from tyrosine supplementation to compensate for low tyrosine levels and support neurotransmitter production.
7. Improves Sleep-Wake Cycles
Sleep regulation: Tyrosine can support alertness when needed, making it useful for individuals dealing with sleep deprivation or irregular sleep schedules. By boosting dopamine and norepinephrine, it helps maintain wakefulness, although it does not directly induce sleep.
8. Improves Mental Clarity in Cold or Altitude Conditions
Extreme environments: Tyrosine has been shown to help individuals maintain cognitive function in extreme environments, such as cold temperatures or high altitudes, where the body is under more physical stress. Supplementing with tyrosine may improve performance and reduce cognitive decline in these conditions.
Conclusion:
Supplementing with tyrosine can be particularly beneficial for improving mental performance under stress, boosting mood, supporting thyroid health, and enhancing physical and cognitive performance. It’s especially helpful for individuals facing stressful or demanding situations, or those with low dopamine levels or hypothyroidism.
Ashwagandha is Important for the Thyroid and Overall Health for the Following Reasons
1. Improves Thyroid Function and Balances Hormones
Thyroid support: Ashwagandha can be beneficial for individuals with hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid). It supports thyroid hormone production (T3 and T4), which can improve metabolism, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Hormonal balance: For women, ashwagandha may help balance hormones, particularly those related to reproductive health. It can reduce symptoms associated with PMS and menopause, such as mood swings and fatigue.
2. Reduces Stress and Anxiety
Adaptogen: Ashwagandha is classified as an adaptogen, meaning it helps the body adapt to stress. It can lower levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, helping to reduce feelings of stress and anxiety.
Anxiety relief: Studies show that ashwagandha can reduce symptoms of anxiety and may help improve overall mood, making it particularly useful for people dealing with chronic stress or anxiety disorders.
3. Improves Sleep Quality
Natural sleep aid: Ashwagandha has calming properties that can improve sleep quality. It promotes relaxation and helps individuals fall asleep faster, making it a natural remedy for insomnia or disrupted sleep.
Balances sleep-wake cycle: By reducing stress and cortisol levels, it helps regulate the body’s natural circadian rhythm, supporting better overall sleep patterns.
4. Boosts Brain Function and Memory
Cognitive enhancement: Ashwagandha is believed to improve cognitive function, memory, and focus. It supports brain health by protecting nerve cells from damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation.
Anti-anxiety effects on cognition: Ashwagandha can help prevent cognitive decline associated with stress and aging. It enhances concentration and supports learning and memory retention.
5. Supports Immune Function
Immune-boosting properties: Ashwagandha helps modulate the immune system, enhancing the body's ability to fight off infections. It also has anti-inflammatory properties, which can reduce chronic inflammation and support overall immune health.
Antioxidant effects: Ashwagandha contains powerful antioxidants that help protect cells from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune response.
6. Boosts Energy and Stamina
Enhances physical performance: Ashwagandha has been shown to increase endurance, strength, and muscle recovery, making it a popular supplement among athletes and individuals looking to improve physical performance.
Reduces fatigue: By reducing stress and improving energy metabolism, ashwagandha helps combat feelings of fatigue, promoting increased energy levels throughout the day.
7. Promotes Heart Health
Reduces cholesterol and blood pressure: Ashwagandha has been found to reduce levels of LDL cholesterol (the "bad" cholesterol) and lower blood pressure, both of which are important for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Improves circulation: By lowering inflammation and promoting better circulation, ashwagandha supports a healthy heart and reduces the risk of heart disease.
8. Helps Manage Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar regulation: Ashwagandha may help lower blood sugar levels in both healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes. It enhances insulin sensitivity, making it easier for the body to regulate blood glucose levels.
Prevents sugar spikes: Its anti-inflammatory properties also support metabolic health by preventing insulin resistance and reducing harmful blood sugar spikes.
9. Supports Sexual and Reproductive Health
Male fertility: Ashwagandha is known to increase testosterone levels in men, which can improve sperm quality, boost fertility, and enhance overall reproductive health.
Female reproductive health: In women, ashwagandha may help balance hormones related to fertility, menstrual health, and overall reproductive function, supporting a healthy hormonal environment.
Conclusion
Ashwagandha is a powerful adaptogenic herb that supports mental and physical health by reducing stress, improving sleep, boosting cognitive function, enhancing immune health, improving thyroid function, and balancing hormones. Whether you're seeking to manage stress, improve sleep, support thyroid health, or enhance overall well-being, ashwagandha can be a valuable supplement in your daily routine. However, it's always important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Bladderwrack is Important for the Thyroid and Overall Health for the Following Reasons
1. Supports Thyroid Health
Rich in iodine: Bladderwrack is an excellent natural source of iodine, a mineral essential for proper thyroid function. The thyroid gland needs iodine to produce the hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which regulate metabolism, energy production, and overall growth.
Helps with hypothyroidism: For individuals with hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), bladderwrack supplementation can help alleviate symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance by providing the iodine needed to boost thyroid hormone production.
2. Boosts Metabolism
Regulates metabolic rate: By supporting healthy thyroid function, bladderwrack helps regulate metabolism. A well-functioning thyroid ensures that the body burns energy efficiently, which is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight and energy levels.
Promotes weight management: People with underactive thyroids often struggle with weight gain and slow metabolism. Bladderwrack supplementation may help increase metabolism and assist with weight management efforts when combined with a healthy diet and exercise.
3. Rich in Antioxidants
Protects against oxidative stress: Bladderwrack is rich in antioxidants, including fucoidan and phlorotannins, which protect the body’s cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. This helps reduce inflammation and lowers the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
Anti-aging properties: The antioxidants in bladderwrack can help combat skin aging, reducing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines, and promoting a more youthful complexion.
4. Supports Digestive Health
Improves digestion: Bladderwrack contains alginate, a type of dietary fiber that helps regulate bowel movements and promote healthy digestion. It can help relieve constipation, bloating, and other digestive issues by encouraging smooth bowel function.
Gut health: The polysaccharides in bladderwrack may support gut health by acting as prebiotics, which feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut and promote a balanced microbiome.
5. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Reduces inflammation: Bladderwrack’s rich content of anti-inflammatory compounds, including fucoidan, helps reduce chronic inflammation in the body. This can be beneficial for conditions like arthritis, where inflammation plays a key role in joint pain and stiffness.
Joint health: The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of bladderwrack can help alleviate joint pain and improve mobility, making it a useful supplement for people with osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
6. Improves Skin Health
Hydrates and nourishes skin: Bladderwrack is often used in skincare products for its hydrating and nourishing properties. It helps soothe irritated or inflamed skin, and its high mineral content (including iodine, potassium, and calcium) promotes healthy skin.
Reduces skin conditions: The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of bladderwrack can help reduce symptoms of conditions like eczema and psoriasis, while also promoting wound healing.
7. Supports Heart Health
Lowers cholesterol: Bladderwrack may help lower levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol while promoting healthy circulation. This is important for reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and atherosclerosis.
Regulates blood pressure: The potassium content in bladderwrack can help regulate blood pressure, preventing hypertension and promoting overall heart health.
8. Supports Eye Health
Rich in beta-carotene: Bladderwrack contains beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A, which is crucial for maintaining healthy vision. Adequate vitamin A intake is important for preventing night blindness and age-related macular degeneration.
9. Provides Essential Minerals
Nutrient-dense: Bladderwrack is packed with essential vitamins and minerals, including iodine, calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc, and vitamins A and C. These nutrients support a wide range of bodily functions, including immune health, bone health, and overall vitality.
Bone health: The calcium and magnesium content in bladderwrack contributes to strong bones and helps prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Bladderwrack is an incredibly nutrient-dense seaweed that offers a range of health benefits, from supporting thyroid function and metabolism to improving skin health, digestion, and joint pain. Its high iodine content makes it particularly useful for people with underactive thyroids or those looking to enhance their overall metabolic function. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting bladderwrack supplementation, especially if you have thyroid conditions, as excessive iodine intake can be harmful.
Guggul Resin (Guggulsterones) Are Important for the Thyroid and Overall Health for the Following Reasons:
Guggul resin, derived from the Commiphora mukul tree, has been used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine for centuries. Guggul contains active compounds called guggulsterones, which have been studied for their potential health benefits. Supplementing with guggul resin or guggulsterones can be important for several reasons, primarily related to metabolic (thyroid) health, inflammation, and cholesterol management:
1. Thyroid Function
Guggulsterones may support healthy thyroid function. Some studies suggest they can stimulate thyroid activity, potentially boosting metabolism and aiding in weight management. This could be beneficial for people with mild hypothyroidism or sluggish metabolism.
2. Cholesterol and Lipid Regulation
Guggulsterones are believed to help regulate cholesterol levels by increasing the uptake of LDL (low-density lipoprotein, or "bad" cholesterol) by the liver and promoting its excretion from the body. This can lead to lower levels of total cholesterol and LDL, which may reduce the risk of heart disease.
3. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Guggulsterones have anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is linked to various health conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, and metabolic disorders. Guggul has been used in traditional medicine to treat inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
4. Antioxidant Effects
Guggul has antioxidant properties, helping to neutralize free radicals and prevent oxidative damage to cells. This can be important for maintaining overall cellular health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
5. Weight Management
Due to its potential effects on metabolism and fat breakdown, guggul supplements may support weight loss efforts, especially when combined with proper diet and exercise.
While guggul has been used traditionally and shows promise in modern research, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement, as it can interact with medications or cause side effects in some individuals.
Inositol is Important for the Thyroid and Overall Health for the Following Reasons:
Inositol supports thyroid function, especially in individuals with certain thyroid-related conditions like subclinical hypothyroidism and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (an autoimmune condition that affects the thyroid). While inositol is not traditionally associated with thyroid health, recent research suggests that it may play a role in supporting thyroid function through the following mechanisms:
1. Improvement in TSH Levels
Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Some studies have shown that supplementing with inositol and selenium can help normalize thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels in individuals with subclinical hypothyroidism. This suggests that inositol might support thyroid function by regulating TSH production, which is essential for the thyroid gland to produce hormones that regulate metabolism.
Support for Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Inositol may also benefit individuals with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism. Inositol, when combined with selenium, has been studied for its potential to reduce thyroid antibody levels (such as anti-TPO antibodies), which can help in reducing inflammation and preserving thyroid function.
3. Antioxidant Effects
Inositol has antioxidant properties that may help reduce oxidative stress, which is known to affect thyroid function negatively. By neutralizing free radicals, inositol may support the thyroid gland's ability to function more efficiently, potentially protecting the gland from damage associated with autoimmune conditions.
4. Improved Hormonal Balance
While inositol is more well-known for its role in insulin sensitivity and hormonal balance, these functions indirectly support thyroid health. Since insulin resistance can influence various hormonal pathways, including those related to thyroid function, improving insulin sensitivity may contribute to better overall endocrine balance.
Conclusion
Though inositol is not a primary treatment for thyroid disorders, it has shown potential benefits, especially when combined with other nutrients like selenium, for individuals with subclinical hypothyroidism and autoimmune thyroid conditions such as Hashimoto’s. Inositol's ability to improve TSH regulation and reduce thyroid antibodies may help support thyroid function, particularly in specific thyroid-related conditions.
As always, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional before starting inositol supplements, particularly if you have thyroid-related health concerns.
Ecklonia Cava is Important for Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Ecklonia cava, a type of brown seaweed found off the coasts of Korea and Japan, is gaining attention for its potential health benefits, including its impact on thyroid health. Ecklonia cava is rich in bioactive compounds, particularly phlorotannins, which are unique antioxidants found in brown algae. Here’s why it may be important for thyroid health:
1. Iodine Content
- Supports Thyroid Hormone Production: Like many seaweeds, Ecklonia cava is a natural source of iodine, an essential nutrient for thyroid function. The thyroid gland uses iodine to produce thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), which are crucial for regulating metabolism, growth, and energy levels. Adequate iodine intake is necessary to prevent thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and goiter (thyroid enlargement).
- Prevents Iodine Deficiency: Iodine deficiency is one of the leading causes of thyroid dysfunction globally. Consuming iodine-rich foods like Ecklonia cava can help ensure that the body has sufficient iodine to maintain normal thyroid function and hormone production.
2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Reduces Thyroid Inflammation: Ecklonia cava contains potent phlorotannins, which have strong anti-inflammatory properties. This is particularly important for thyroid health because inflammation can exacerbate thyroid conditions, such as Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland. Reducing inflammation in the thyroid may help improve its function and prevent further damage to thyroid tissue.
3. Antioxidant Support
Protects Against Oxidative Stress: Phlorotannins in Ecklonia cava are powerful antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress can contribute to the development of thyroid disorders, including Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. By protecting the thyroid from oxidative damage, Ecklonia cava may help preserve thyroid function and overall endocrine health.
Thyroid Gland Protection: Since the thyroid is a highly vascularized and metabolically active gland, it is especially susceptible to oxidative stress. The antioxidant properties of Ecklonia cava may protect thyroid cells from oxidative damage and inflammation, which can lead to dysfunction over time.
4. Supports Metabolic Health
- Helps with Weight Management: Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, and an underactive thyroid can lead to weight gain and difficulty losing weight. The metabolism-boosting properties of iodine, combined with Ecklonia cava’s potential effects on improving insulin sensitivity and reducing fat accumulation, may help support healthier metabolism in people with thyroid issues.
- Fat Metabolism: Ecklonia cava has also been studied for its potential role in promoting healthy fat metabolism and weight loss, which can be especially beneficial for people with hypothyroidism, where slowed metabolism often results in weight gain.
5. Potential Thyroid-Stimulating Effects
Stimulates Thyroid Hormone Production: Some studies suggest that Ecklonia cava might have the ability to stimulate thyroid activity, possibly through its iodine content or other bioactive compounds. This may make it beneficial for individuals with suboptimal thyroid function or hypothyroidism.
6. Supports Cardiovascular Health
Reduces Cholesterol and Blood Pressure: Thyroid disorders, especially hypothyroidism, are often associated with high cholesterol levels and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Ecklonia cava has been shown to have cholesterol-lowering and blood pressure-reducing properties, which could indirectly benefit individuals with thyroid conditions by improving cardiovascular health.
Conclusion - Ecklonia Cava - Thyroid
Ecklonia cava is important for thyroid health due to its rich content of iodine, phlorotannins, and antioxidants. It helps support thyroid hormone production, reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the thyroid gland, and promote overall metabolic and cardiovascular health. This seaweed could be especially beneficial for individuals with thyroid conditions like hypothyroidism or Hashimoto's thyroiditis, as it provides natural iodine and anti-inflammatory compounds to support thyroid function and protect against further damage.
However, as with any supplement, it's important to consult a healthcare professional before using Ecklonia cava, especially if you have thyroid issues, as excess iodine intake can potentially lead to thyroid imbalances.
Iodine is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Iodine is essential for thyroid health because it plays a key role in the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate many bodily functions, including metabolism, growth, and development. Here's why iodine is critical for thyroid health:
1. Essential for Thyroid Hormone Production
- The thyroid gland uses iodine to produce two primary hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4): Contains four iodine atoms.
- Triiodothyronine (T3): Contains three iodine atoms and is the active form of the hormone.
- Iodine is required for the synthesis of both T4 and T3. Without adequate iodine, the thyroid cannot produce enough hormones, leading to thyroid dysfunction.
2. Prevents Hypothyroidism
- Iodine deficiency is one of the most common causes of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid), where the thyroid doesn't produce enough hormones. This can result in symptoms like:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Slowed heart rate
- Ensuring sufficient iodine intake helps the thyroid maintain normal hormone production, preventing hypothyroidism.
3. Prevents Goiter
A goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland, often caused by iodine deficiency. When the thyroid does not receive enough iodine, it tries to compensate by growing larger in an effort to trap more iodine from the bloodstream.
Adequate iodine intake reduces the risk of goiter and helps the thyroid maintain its normal size and function.
4. Supports Metabolic Regulation
Thyroid hormones regulate the body's metabolism. These hormones control how cells convert nutrients into energy and regulate key metabolic processes.
Iodine is essential for the thyroid to produce enough hormones to regulate metabolism effectively. Without iodine, metabolism can slow down, leading to weight gain and other metabolic issues.
5. Critical for Brain Development in Infants
- During pregnancy and early childhood, iodine is essential for proper brain development. Thyroid hormones, which depend on iodine, are necessary for fetal and infant brain development. Iodine deficiency during pregnancy can result in:
- Cretinism: A condition of severely stunted physical and mental growth due to untreated congenital hypothyroidism.
- Cognitive impairments and developmental delays in infants.
- Pregnant women need to ensure they have adequate iodine intake to support fetal development and prevent neurological disorders in newborns.
6. Prevents Mental and Cognitive Decline
Iodine deficiency, especially during pregnancy or in early childhood, can lead to lower IQ and impaired cognitive function. Adequate iodine intake supports healthy brain function and overall cognitive health.
Studies have shown that iodine supplementation can improve cognitive function in iodine-deficient populations, particularly in children.
7. Maintains Hormonal Balance
Proper iodine intake ensures that the thyroid produces hormones in the right amounts, preventing hormonal imbalances that can affect mood, energy levels, and overall health.
Iodine helps the thyroid produce and release hormones in response to the body’s needs, maintaining balanced hormone levels in the bloodstream.
8. Protects Against Autoimmune Thyroid Disorders
Iodine plays a role in regulating immune responses in the thyroid. Both iodine deficiency and excess can lead to thyroid dysfunction. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune hypothyroidism) and Graves’ disease (autoimmune hyperthyroidism) can be triggered by abnormal iodine levels.
Maintaining an optimal iodine intake helps protect against these autoimmune thyroid disorders, ensuring a balanced immune response in the thyroid.
Conclusion as to the Importance of Iodine for Thyroid Health
Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, brain development, and many other critical functions in the body. Without adequate iodine, thyroid hormone production declines, leading to conditions like hypothyroidism, goiter, and cognitive impairments. Ensuring sufficient iodine intake through diet or supplements is vital for maintaining thyroid health and overall well-being.
Common dietary sources of iodine include iodized salt, seafood, dairy products, and eggs. It's important to consult a healthcare professional if you are concerned about iodine levels, as both iodine deficiency and excess can impact thyroid function.
Selenium is Important for Thyroid and Overall Health for Thease Reasons
Selenium is a crucial mineral for thyroid health because it plays several essential roles in the proper functioning and protection of the thyroid gland. Here are the key reasons why selenium is important for thyroid health:
1. Thyroid Hormone Production and Conversion
- Selenium-Dependent Enzymes: Selenium is a critical component of enzymes called selenoproteins, particularly the enzyme iodothyronine deiodinase, which is responsible for converting thyroxine (T4), the inactive thyroid hormone, into its active form, triiodothyronine (T3). T3 is the more potent thyroid hormone and is necessary for regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall thyroid function.
- Optimizes Hormone Balance: Without adequate selenium, this conversion process can be impaired, leading to a reduced availability of T3 and potential symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, weight gain, and slowed metabolism.
2. Antioxidant Protection for the Thyroid
- Neutralizes Free Radicals: The thyroid gland is highly metabolically active and generates large amounts of hydrogen peroxide during the production of thyroid hormones. Selenium, as part of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase, helps neutralize these free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), protecting the thyroid from oxidative stress and damage.
- Prevents Inflammation: By reducing oxidative stress, selenium helps prevent inflammation in the thyroid, which can contribute to autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease. Protecting the thyroid from oxidative damage helps maintain its overall function and longevity.
3. Reduces Thyroid Antibodies in Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
- Autoimmune Thyroid Support: Selenium supplementation has been shown to reduce levels of thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) and thyroglobulin antibodies (TgAb) in individuals with Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the thyroid. Lower antibody levels can reduce inflammation and slow the progression of thyroid damage.
- Graves’ Disease Management: Selenium may also be beneficial for individuals with Graves' disease, an autoimmune condition that causes hyperthyroidism. It can help reduce inflammation and improve overall thyroid function in people with overactive thyroids as well.
4. Supports Immune Function
- Immune Regulation: Selenium plays a role in modulating the immune system, ensuring that it functions properly without becoming overactive and attacking the body’s tissues, as seen in autoimmune thyroid disorders. This immune-regulating effect is vital for preventing and managing conditions like Hashimoto's and Graves' disease.
- Thyroid Immune Response: By supporting a healthy immune response, selenium may reduce the risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases or lessen the severity of existing conditions.
5. Thyroid Health in Pregnancy
- Protects the Mother and Fetus: During pregnancy, selenium is particularly important for maintaining thyroid health in both the mother and developing fetus. Adequate selenium levels help prevent thyroid dysfunction, such as postpartum thyroiditis and hypothyroidism, which can negatively affect the mother’s health and fetal development.
- Fetal Brain Development: Selenium is also essential for proper brain development in the fetus, as thyroid hormones (which require selenium for activation) play a critical role in neurological development during pregnancy.
6. Reduces Risk of Goiter
- Prevents Goiter: Goiter (thyroid enlargement) can develop as a result of selenium deficiency, particularly when iodine intake is low. Selenium helps maintain optimal thyroid function and hormone production, reducing the risk of thyroid enlargement and related conditions.
7. Works Synergistically with Iodine
- Complementary Role to Iodine: While iodine is essential for producing thyroid hormones, selenium is necessary for converting these hormones into their active form and protecting the thyroid gland. Selenium works in tandem with iodine to support overall thyroid health, and deficiency in one or both can lead to thyroid dysfunction.
Conclusion as to the Role of Selenium in Thyroid Health
Selenium is vital for thyroid hormone production, conversion, and protection from oxidative stress. It plays a key role in immune regulation, particularly in autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease, by reducing thyroid antibodies and inflammation. Selenium also supports thyroid health during pregnancy and works synergistically with iodine to ensure optimal thyroid function.
Due to its essential role, ensuring an adequate intake of selenium through diet or supplements can be crucial for maintaining healthy thyroid function, especially for individuals with thyroid disorders. However, selenium should be taken with caution, as excessive intake can lead to toxicity. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting selenium supplementation is advisable, particularly if you have thyroid-related health concerns.
Copper is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons
Copper is important for thyroid health, although its role is not as widely discussed as that of iodine or selenium. Copper is an essential trace mineral that supports various physiological processes, some of which are indirectly related to thyroid function. Here are the key reasons why copper is important for thyroid health:
1. Thyroid Hormone Production and Regulation
- Enzyme Activation: Copper plays a role in activating enzymes that are important for thyroid hormone synthesis. While iodine is the primary nutrient involved in thyroid hormone production, copper helps activate enzymes that facilitate the incorporation of iodine into thyroid hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
- Maintains Hormonal Balance: Copper helps balance thyroid hormones in the bloodstream, ensuring that thyroid hormone production is neither too high (hyperthyroidism) nor too low (hypothyroidism).
2. Antioxidant Protection for the Thyroid
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Enzyme: Copper is an essential component of the enzyme copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (CuZn-SOD), which acts as an antioxidant in the body. This enzyme helps protect cells, including those in the thyroid gland, from oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
- Thyroid Gland Protection: The thyroid is a highly active organ that is susceptible to oxidative damage, especially during thyroid hormone production. Copper’s role in SOD helps neutralize these free radicals, protecting the thyroid from potential damage, which could otherwise lead to dysfunction or thyroid diseases.
3. Supports Iron Metabolism and Thyroid Function
- Iron Absorption and Utilization: Copper is essential for the body’s ability to absorb and utilize iron, which is also important for thyroid health. Iron deficiency can impair thyroid hormone production, leading to hypothyroidism. Copper helps regulate iron metabolism by supporting the synthesis of hemoglobin and ensuring proper oxygen transport, which indirectly affects thyroid function.
- Prevents Anemia-Related Thyroid Issues: Since anemia (caused by iron deficiency) can affect thyroid function, copper helps by ensuring that iron levels are adequate, reducing the risk of anemia-related thyroid problems.
4. Nervous System Support
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Copper is involved in the production of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which influence brain function and mood regulation. Since thyroid hormones also play a role in brain health and mood stability, copper’s role in neurotransmitter production indirectly supports the neurological aspects of thyroid health.
5. Energy Production
- Mitochondrial Function: Copper is essential for mitochondrial function, where it helps produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body's main energy currency. Since the thyroid gland regulates metabolism and energy production through the release of thyroid hormones, copper’s role in mitochondrial function supports overall energy metabolism, which is directly influenced by thyroid health.
6. Maintains Immune System Function
- Immune Regulation: Copper supports the immune system by contributing to the production and function of white blood cells. Since autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis and Graves' disease involve immune dysfunction, maintaining proper copper levels helps support the immune system and potentially reduce the risk of thyroid-related autoimmune issues.
7. Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Regulation
Copper may help regulate the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland. TSH is responsible for signaling the thyroid to produce T3 and T4 hormones. Proper copper levels ensure that TSH release is balanced, which is crucial for healthy thyroid function.
Conclusion As to the Role of Copper in Thyroid Health
Copper is important for thyroid health due to its role in enzyme activation, antioxidant defense, iron metabolism, and energy production. It helps protect the thyroid from oxidative damage, supports hormone balance, and ensures efficient energy metabolism. Additionally, copper plays an indirect role in maintaining proper immune function and nervous system health, which are important factors in thyroid health.
While copper is an essential nutrient, it is important to maintain balanced levels, as both copper deficiency and excess can lead to health issues, including thyroid dysfunction. If you are concerned about copper levels and thyroid health, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare provider before considering supplementation.
Manganese Is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Manganese plays a supportive role in overall health, including thyroid health, although its impact on the thyroid is not as direct or well-known as that of other minerals like iodine and selenium. However, manganese is still important for thyroid function because it serves as a cofactor for several enzymes involved in antioxidant defense, metabolism, and hormone regulation, all of which indirectly influence thyroid health. Here are the key reasons why manganese is important for thyroid health:
1. Antioxidant Defense and Thyroid Protection
- Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Enzyme: Manganese is a crucial cofactor for the manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) enzyme, one of the primary antioxidants in the body. This enzyme helps neutralize free radicals (reactive oxygen species) that can cause oxidative stress.
- Thyroid Gland Protection: Since the thyroid is highly metabolically active, it is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress. Manganese supports the function of MnSOD, helping to protect the thyroid gland from oxidative damage, which can contribute to thyroid dysfunction and autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
2. Metabolism and Energy Regulation
- Thyroid Hormone Regulation: While manganese is not directly involved in thyroid hormone production like iodine or selenium, it plays a role in regulating metabolic processes that are closely linked to thyroid function. The thyroid gland regulates metabolism through the release of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), and manganese is involved in several metabolic enzymes that help process carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, influencing overall metabolic rate.
- Energy Production: Manganese is necessary for the activity of enzymes that support mitochondrial function (energy production in cells), which is indirectly tied to thyroid health, as the thyroid controls the body’s energy expenditure.
3. Bone Health and Thyroid Interaction
- Bone Metabolism: Manganese is involved in bone health, and there is a known interaction between thyroid function and bone metabolism. An imbalance in thyroid hormones (such as hyperthyroidism) can lead to bone loss, while manganese helps support bone density and health. Maintaining healthy manganese levels can contribute to the protection of bone health, which is especially important for individuals with thyroid disorders that may affect bone integrity.
4. Supports Nervous System Health
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: Manganese is essential for the production of neurotransmitters, including dopamine and glutamate, which are important for brain function and mood regulation. Thyroid hormones also influence brain function, and imbalances can lead to mood changes, depression, and cognitive issues. Manganese's role in neurotransmitter production indirectly supports overall mental well-being, which can be affected by thyroid health.
5. Synergistic Role with Other Minerals
- Works with Iodine and Selenium: Manganese works alongside other essential minerals like iodine, selenium, and zinc to support thyroid and metabolic health. While manganese does not directly influence thyroid hormone production, maintaining the right balance of these minerals is crucial for overall endocrine function.
Conclusion Regarding Importance of Manganese to Thyroid Healthy and Function
While manganese does not play as central a role in thyroid function as iodine or selenium, it is important for maintaining overall metabolic health, providing antioxidant protection to the thyroid, supporting energy production, and promoting healthy bone and nervous system function. By contributing to these areas, manganese indirectly supports the health and proper functioning of the thyroid gland.
As with all minerals, maintaining a balanced intake is key, as both deficiencies and excesses can negatively affect health. If you are concerned about your manganese levels and thyroid function, it's a good idea to consult a healthcare provider before considering supplementation.
Molybdenum Is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Molybdenum is important for thyroid health due to its role in several biochemical processes that indirectly support thyroid function. Here are some reasons why molybdenum may play a role in thyroid health:
1. Cofactor for Detoxification Enzymes
Molybdenum acts as a cofactor for enzymes such as sulfite oxidase, which is involved in detoxifying sulfites. By aiding in detoxification processes, molybdenum helps reduce oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress can negatively affect thyroid cells, leading to thyroid dysfunction. Proper detoxification supports overall metabolic health, which is closely linked to thyroid function.
2. Support for Sulfur Metabolism
Molybdenum is involved in sulfur metabolism through its action on sulfite oxidase, which breaks down sulfur-containing compounds. The thyroid gland is sensitive to disruptions in sulfur metabolism. Sulfur compounds, when improperly metabolized, can cause oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially affecting thyroid function. Molybdenum ensures that sulfur metabolism runs smoothly, thereby supporting thyroid health.
3. Interaction with Selenium
Selenium is crucial for thyroid hormone metabolism, particularly for the conversion of T4 (thyroxine) to T3 (triiodothyronine), the active form of thyroid hormone. Molybdenum may interact with selenium, potentially influencing its bioavailability and, in turn, thyroid hormone production. Although selenium is the more recognized element in this process, molybdenum’s interaction with selenium may indirectly affect thyroid hormone levels.
4. Iodine Utilization
Iodine is a key element needed for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Some research suggests that molybdenum may influence iodine metabolism. Proper iodine utilization is essential for the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), and any imbalance can lead to thyroid disorders. Molybdenum may help regulate iodine absorption and utilization, preventing imbalances that could lead to thyroid dysfunction.
5. Reducing Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress can harm thyroid cells and contribute to conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis (an autoimmune disorder) or Graves' disease. Molybdenum's role in detoxification enzymes helps the body reduce oxidative stress, thus potentially preventing damage to thyroid tissues.
Conclusions Regarding Molybdenum's Contribution to Thyroid Health
Molybdenum’s contribution to detoxification, sulfur metabolism, and its interactions with key elements like selenium and iodine make it an important mineral for maintaining healthy thyroid function. While more research is needed to fully understand its direct impact, molybdenum is considered to play a supportive role in thyroid health, largely through its influence on broader metabolic and detoxification processes.
Zinc Is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Zinc plays a crucial role in supporting the normal functioning of the thyroid gland, which is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and energy levels in the body. Here’s how zinc contributes to thyroid health:
- Thyroid Hormone Production: Zinc is involved in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, particularly the conversion of thyroxine (T4) into the more active form, triiodothyronine (T3). This conversion is essential for maintaining optimal metabolic functions.
- Immune Function and Inflammation Control: Since zinc is important for a healthy immune system, it helps prevent chronic inflammation, which can negatively impact thyroid function. Autoimmune thyroid disorders, like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves' disease, are related to immune dysfunction, and zinc helps in regulating immune responses.
- Thyroid Receptor Sensitivity: Zinc also plays a role in improving the sensitivity of cells to thyroid hormones, allowing the body to utilize the hormones effectively.
- Regulation of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): Zinc influences the production of TSH from the pituitary gland, which helps regulate thyroid hormone levels.
A deficiency in zinc can lead to symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance, even if thyroid hormone levels are normal. It’s important to maintain adequate levels of zinc, either through diet or supplementation, for overall thyroid health.
Vitamin is Important to Thyroid Health for the Following Reasons:
Yes, Vitamin A plays an important role in thyroid health. Its benefits come from its interaction with thyroid hormones and its role in the regulation of certain genes. Here are some key ways Vitamin A supports thyroid health:
1. Regulation of Thyroid Hormone Metabolism
Vitamin A helps regulate the synthesis of thyroid hormones by influencing the activity of the pituitary gland. The pituitary releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which signals the thyroid gland to produce and release thyroid hormones. Studies show that Vitamin A deficiency can lead to increased levels of TSH, which suggests that the thyroid might be working harder to produce hormones when Vitamin A levels are low. Adequate Vitamin A can help maintain proper levels of TSH, which in turn supports balanced thyroid hormone production.
2. Interaction with Iodine
Iodine is critical for thyroid function because it's needed for the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Some research indicates that Vitamin A enhances the utilization of iodine in the thyroid gland, helping to support healthy thyroid hormone synthesis. A study conducted in iodine-deficient areas found that supplementing with both Vitamin A and iodine had a more significant effect on reducing goiter and improving thyroid function than iodine alone.
3. Regulation of Thyroid Receptors
Vitamin A plays a role in regulating the expression of thyroid hormone receptors, particularly in tissues like the liver. This interaction is important because it ensures that thyroid hormones can properly bind to their receptors and exert their effects on metabolic regulation, growth, and energy production. If Vitamin A is lacking, the ability of cells to properly respond to thyroid hormones may be impaired, even if thyroid hormone levels are normal.
4. Antioxidant Effects and Immune Support
Vitamin A is also an antioxidant, which helps reduce oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can lead to inflammation in the thyroid gland and may be associated with autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease. By reducing inflammation and supporting immune function, Vitamin A may help protect the thyroid from damage caused by chronic inflammation.
5. Support for Conversion of T4 to T3
The thyroid produces mostly T4 (thyroxine), which must be converted into the active form T3 (triiodothyronine) to be used by the body. Vitamin A supports this conversion process, ensuring that adequate levels of active thyroid hormones are available for metabolism and other functions.
Conclusion as to Benefits of Vitamin A in Regard to Thyroid Health
Vitamin A is beneficial for thyroid health by supporting thyroid hormone metabolism, enhancing iodine utilization, regulating thyroid receptors, and providing antioxidant protection. Adequate Vitamin A intake can contribute to maintaining healthy thyroid function, and its deficiency may be linked to thyroid imbalances. For those with thyroid concerns, ensuring proper Vitamin A levels through diet or supplementation may be beneficial, but it's always best to consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Thyroid Resilience Ordering Form
Comparative Retail Price: $39.95
Our Price: $31.00
Thyroid Resilience
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

How to Use
- One or two capsules twice a day with 6-8 ounces of water.
Videos and Audios about Thyroid Resilience
We disclaim any claims (if there are any) made in these videos or audios. They are for information, education, enlightenment and entertainment only.


